- Lesotho
-
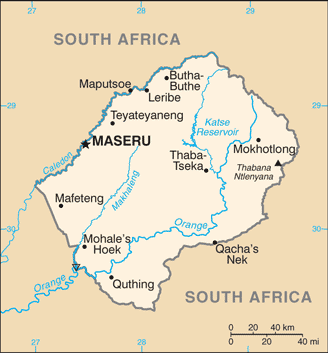 Introduction ::LesothoBackground:Basutoland was renamed the Kingdom of Lesotho upon independence from the UK in 1966. The Basuto National Party ruled the country during its first two decades. King MOSHOESHOE was exiled in 1990, but returned to Lesotho in 1992 and was reinstated in 1995 and subsequently succeeded by his son, King LETSIE III, in 1996. Constitutional government was restored in 1993 after seven years of military rule. In 1998, violent protests and a military mutiny following a contentious election prompted a brief but bloody intervention by South African and Batswana military forces under the aegis of the Southern African Development Community. Subsequent constitutional reforms restored relative political stability. Peaceful parliamentary elections were held in 2002, but the National Assembly elections of February 2007 were hotly contested and aggrieved parties disputed how the electoral law was applied to award proportional seats in the Assembly. In May 2012, competitive elections involving 18 parties saw Prime Minister Motsoahae Thomas THABANE form a coalition government - the first in the country's history - that ousted the 14-year incumbent, Pakalitha MOSISILI, who peacefully transferred power the following month.Geography ::LesothoLocation:Southern Africa, an enclave of South AfricaGeographic coordinates:29 30 S, 28 30 EArea:total: 30,355 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 142land: 30,355 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than MarylandLand boundaries:total: 909 kmborder countries: South Africa 909 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:temperate; cool to cold, dry winters; hot, wet summersTerrain:mostly highland with plateaus, hills, and mountainsElevation extremes:lowest point: junction of the Orange and Makhaleng Rivers 1,400 mhighest point: Thabana Ntlenyana 3,482 mNatural resources:water, agricultural and grazing land, diamonds, sand, clay, building stoneLand use:arable land: 10.14%permanent crops: 0.13%other: 89.72% (2011)Irrigated land:26.37 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:3.02 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 0.04 cu km/yr (46%/46%/9%)per capita: 21.79 cu m/yr (2000)Natural hazards:periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:population pressure forcing settlement in marginal areas results in overgrazing, severe soil erosion, and soil exhaustion; desertification; Highlands Water Project controls, stores, and redirects water to South AfricaEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:landlocked, completely surrounded by South Africa; mountainous, more than 80% of the country is 1,800 m above sea levelPeople and Society ::LesothoNationality:noun: Mosotho (singular), Basotho (plural)adjective: BasothoEthnic groups:Sotho 99.7%, Europeans, Asians, and other 0.3%,Languages:Sesotho (official) (southern Sotho), English (official), Zulu, XhosaReligions:Christian 80%, indigenous beliefs 20%Population:1,936,181 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 148note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 33.1% (male 322,189/female 319,618)15-24 years: 20.2% (male 185,931/female 205,643)25-54 years: 36.3% (male 344,120/female 359,370)55-64 years: 4.9% (male 50,781/female 44,399)65 years and over: 5.4% (male 52,241/female 51,889) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 68.3 %youth dependency ratio: 61.2 %elderly dependency ratio: 7.1 %potential support ratio: 14.1 (2013)Median age:total: 23.4 yearsmale: 23.3 yearsfemale: 23.4 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.34% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Birth rate:26.31 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Death rate:15.02 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Net migration rate:-7.89 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Urbanization:urban population: 27.6% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.57% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MASERU (capital) 220,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.9 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.14 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.99 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:21.2note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2009 est.)Maternal mortality rate:620 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 12Infant mortality rate:total: 51.93 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 38male: 55.96 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 47.78 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 52.3 yearscountry comparison to the world: 212male: 52.2 yearsfemale: 52.39 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.83 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Contraceptive prevalence rate:47% (2009/10)Health expenditures:11.1% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 18Physicians density:0.05 physicians/1,000 population (2003)Hospital bed density:1.33 beds/1,000 population (2006)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 91% of populationrural: 73% of populationtotal: 78% of populationunimproved:urban: 9% of populationrural: 27% of populationtotal: 22% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 32% of populationrural: 24% of populationtotal: 26% of populationunimproved:urban: 68% of populationrural: 76% of populationtotal: 74% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:23.6% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 3HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:290,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 20HIV/AIDS - deaths:14,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Obesity - adult prevalence rate:14.6% (2008)country comparison to the world: 120Children under the age of 5 years underweight:13.5% (2010)country comparison to the world: 56Education expenditures:13% of GDP (2008)country comparison to the world: 1Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 89.6%male: 83.3%female: 95.6% (2010 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 10 yearsmale: 10 yearsfemale: 10 years (2006)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 103,020percentage: 23 % (2000 est.)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 34.4%country comparison to the world: 17male: 29%female: 41.9% (2008)Government ::LesothoCountry name:conventional long form: Kingdom of Lesothoconventional short form: Lesotholocal long form: Kingdom of Lesotholocal short form: Lesothoformer: BasutolandGovernment type:parliamentary constitutional monarchyCapital:name: Maserugeographic coordinates: 29 19 S, 27 29 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:10 districts; Berea, Butha-Buthe, Leribe, Mafeteng, Maseru, Mohale's Hoek, Mokhotlong, Qacha's Nek, Quthing, Thaba-TsekaIndependence:4 October 1966 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 4 October (1966)Constitution:2 April 1993Legal system:mixed legal system of English common law and Roman-Dutch law; judicial review of legislative acts in High Court and Court of AppealInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: King LETSIE III (since 7 February 1996); note - King LETSIE III formerly occupied the throne from November 1990 to February 1995 while his father was in exilehead of government: Prime Minister Motsoahae Thomas THABANE (since 8 June 2012)cabinet: Cabinet(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: according to the constitution, the leader of the majority party, or coalition of parties, in the Assembly automatically becomes prime minister; the monarchy is hereditary, but, under the terms of the constitution that came into effect after the March 1993 election, the monarch is a ""living symbol of national unity"" with no executive or legislative powers; under traditional law the college of chiefs has the power to depose the monarch, determine who is next in the line of succession, or who shall serve as regent in the event that the successor is not of mature ageLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (33 members - 22 principal chiefs and 11 other members appointed by the ruling party) and the Assembly (120 seats, 80 by popular vote and 40 by proportional vote; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)elections: last held on 26 May 2012 (next to be held in 2017)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - DC 48, ABC 30, LCD 26, BNP 5, PFD 3, NIP 2, other 6Judicial branch:highest court(s): Court of Appeal (consists of the court president, such number of justices of appeal as set by Parliament, and the Chief Justice and the puisne judges of the High Court ex officio); High Court (consists of the chief justice and such number of puisne judges as set by Parliament); note - both the Court of Appeal and the High Court have jurisdiction in constitutional issuesjudge selection and term of office: Court of Appeal president and High Court chief justice appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister; puisne judges appointed by the monarch on advice of the Judicial Service Commission, an independent body of judicial officers and officials designated by the monarch; judges of both courts can serve until age 75subordinate courts: Magistrate Courts; customary or traditional courts; Courts MartialPolitical parties and leaders:All Basotho Convention or ABC [Motsoahae Thomas THABANE]Basotho Batho Democratic Party or BBDP [Geremane RAMATHEBANE]Basotho Congress Party or BCP [Thulo MAHLAKENG]Basotho Democratic National Party or BDNP [Thabang NYEOE]Basotho National Party or BNP [Thesele 'MASERIBANE]Democratic Congress or DC [Pakalitha MOSISILI]Lesotho Congress for Democracy or LCD [Mothetjoa METSING]Lesotho Peoples Congress or LPC [Kelebone MAOPE]Lesotho Workers Party or LWP [Macaefa BILLY]Marematlou Freedom Party or MFP [Vincent MALEBO]National Independent Party or NIP [Kimetso MATHABA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Media Institute of Southern Africa, Lesotho chapter [Tsebo MATŠASA] (pushes for media freedom)International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, SACU, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Eliachim Molapi SEBATANEchancery: 2511 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 797-5533FAX: [1] (202) 234-6815Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Carl B. FOXembassy: 254 Kingsway Road, Maseru West (Consular Section)mailing address: P. O. Box 333, Maseru 100, Lesothotelephone: [266] 22 312666FAX: [266] 22 310116Flag description:three horizontal stripes of blue (top), white, and green in the proportions of 3:4:3; the colors represent rain, peace, and prosperity respectively; centered in the white stripe is a black Basotho hat representing the indigenous people; the flag was unfurled in October 2006 to celebrate 40 years of independenceNational symbol(s):Basotho hatNational anthem:name: ""Lesotho fatse la bo ntat'a rona"" (Lesotho, Land of Our Fathers)lyrics/music: Francois COILLARD/Ferdinand-Samuel LAURnote: adopted 1967; the anthem's music derives from an 1823 Swiss songbookEconomy ::LesothoEconomy - overview:Small, mountainous, and completely landlocked by South Africa, Lesotho is a least developed country in which about three-fourths of the people live in rural areas and engage in subsistence agriculture. Lesotho produces less than 20% of the nation's demand for food. Rain-fed agriculture is vulnerable to weather and climate variability; an estimated 725,500 people will require food assistance in 2012/13. The distribution of income in Lesotho remains inequitable. Lesotho relies on South Africa for much of its economic activity. Lesotho imports 90% of the goods it consumes from South Africa, including most agricultural inputs. Households depend heavily on remittances from family members working in South Africa, in mines, on farms and as domestic workers, though mining employment has declined substantially since the 1990s. Government revenue depends heavily on transfers from South Africa. Customs duties from the Southern Africa Customs Union accounted for 44% of government revenue in 2012. The South African Government also pays royalties for water transferred to South Africa from a dam and reservoir system in Lesotho. However, the government continues to strengthen its tax system to reduce dependency on customs duties and other transfers. Access to credit remains a problem for the private sector. The government maintains a large presence in the economy - public expenditures accounted for 55% of GDP in 2010 and the government remains Lesotho's largest employer. Lesotho's largest private employer is the textile and garment industry - approximately 36,000 Basotho, mainly women, work in factories producing garments for export to South Africa and the US. Diamond mining in Lesotho has grown in recent years and may contribute 8.5% to GDP by 2015, according to current forecasts. Lesotho's $362.5 million Millennium Challenge Account Compact, which focused on strengthening the healthcare system, developing the private sector, and providing access to improved water supplies and sanitation facilities, will end in September 2013. Despite the 2008/09 global economic crisis, the economy has recovered strongly with growth averaging nearly 5% per year since 2010.GDP (purchasing power parity):$4.131 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 175$3.972 billion (2011 est.)$3.758 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$2.439 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 775.7% (2011 est.)6.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$2,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 191$2,100 (2011 est.)$2,000 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:21.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 679.4% of GDP (2011 est.)8.7% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 97.2%government consumption: 33.9%investment in fixed capital: 37.3%investment in inventories: -0.1%exports of goods and services: 50.9%imports of goods and services: -118.3%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 6.4%industry: 34.6%services: 59% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:corn, wheat, pulses, sorghum, barley; livestockIndustries:food, beverages, textiles, apparel assembly, handicrafts, construction, tourismIndustrial production growth rate:6.6% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Labor force:894,500 (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 86%industry and services: 14%note: most of resident population engaged in subsistence agriculture; roughly 35% of the active male wage earners work in South Africa (2002 est.)Unemployment rate:25% (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 17445% (2002 est.)Population below poverty line:49% (1999)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1%highest 10%: 39.4% (2003)Distribution of family income - Gini index:63.2 (1995)country comparison to the world: 156 (1986-87)Budget:revenues: $1.658 billionexpenditures: $1.536 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:68% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13Public debt:NAFiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchInflation rate (consumer prices):6.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1635% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:9.36% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2410% (31 December 2010 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:10.08% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8510.4% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$408.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 161$346.5 million (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$897 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 171$820.4 million (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$82.19 million (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 187$60.61 million (31 December 2010 est.)Current account balance:-$352.6 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 88-$521.5 million (2011 est.)Exports:$1.03 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 156$1.003 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:manufactures (clothing, footwear), wool and mohair, food and live animals, electricity, water, diamondsImports:$2.404 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 157$2.296 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:food; building materials, vehicles, machinery, medicines, petroleum productsReserves of foreign exchange and gold:$1.023 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 134$954.5 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$778.6 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 166$791.9 million (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$242 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 100$120 million (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:maloti (LSL) per US dollar -8.2031 (2012 est.)7.26 (2011 est.)7.32 (2010 est.)8.47 (2009)7.75 (2008)Energy ::LesothoElectricity - production:200 million kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 181Electricity - consumption:293 million kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Electricity - imports:121 million kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Electricity - installed generating capacity:76,000 kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Electricity - from fossil fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 149Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 156Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 155Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 197Refined petroleum products - consumption:1,777 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Refined petroleum products - imports:1,813 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 155Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 134Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 159Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:282,100 Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 190Communications ::LesothoTelephones - main lines in use:38,600 (2011)country comparison to the world: 168Telephones - mobile cellular:1.232 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 152Telephone system:general assessment: rudimentary system consisting of a modest number of landlines, a small microwave radio relay system, and a small radiotelephone communication system; mobile-cellular telephone system is expandingdomestic: privatized in 2001, Telecom Lesotho was tasked with providing an additional 50,000 fixed-line connections within five years, a target not met; mobile-cellular service dominates the market and is expanding with a subscribership roughly 65 per 100 persons in 2011; rural services are scantinternational: country code - 266; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:1 state-owned TV station and 2 state-owned radio stations; government controls most private broadcast media; satellite TV subscription service available; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters obtainable (2008)Internet country code:.lsInternet hosts:11,030 (2012)country comparison to the world: 131Internet users:76,800 (2009)country comparison to the world: 168Transportation ::LesothoAirports:24 (2013)country comparison to the world: 132Airports - with paved runways:total: 3over 3,047 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 21914 to 1,523 m: 5under 914 m:16 (2013)Roadways:total: 7,091 kmcountry comparison to the world: 146paved: 1,404 kmunpaved: 5,687 km (2003)Military ::LesothoMilitary branches:Lesotho Defense Force (LDF): Army (includes Air Wing) (2012)Military service age and obligation:18-24 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; women serve as commissioned officers (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 472,456females age 16-49: 508,953 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 270,184females age 16-49: 275,734 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 19,110female: 20,037 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.9% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 70Military - note:Lesotho's declared policy is maintenance of its independent sovereignty and preservation of internal security; in practice, external security is guaranteed by South Africa; restructuring of the Lesotho Defense Force (LDF) and Ministry of Defense and Public Service over the past five years has focused on subordinating the defense apparatus to civilian control and restoring the LDF's cohesion; the restructuring has considerably improved capabilities and professionalism, but the LDF is disproportionately large for a small, poor country; the government has outlined a reduction to a planned 1,500-man strength, but these plans have met with vociferous resistance from the political opposition and from inside the LDF (2008)Transnational Issues ::LesothoDisputes - international:South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migrationTrafficking in persons:current situation: Lesotho is a source, transit, and destination country for women and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking and for men subjected to forced labor; Basotho women and children are subjected to domestic servitude and children, to a lesser extent, commercial sexual exploitation within Lesotho and South Africa; some Basotho women willingly migrate to South Africa seeking work in domestic service only to be forced into prostitution; some Basotho men who voluntarily migrate to South Africa for work become victims of forced labor in agriculture and mining or are coerced into committing crimestier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Lesotho does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government has decreased its anti-trafficking law enforcement and victim protection efforts during 2012; authorities have initiated fewer prosecutions, ceased arresting suspected trafficking offenders due to a backlog of prosecutions, and stopped referring victims to NGO centers for care; the government has not implemented key portions of the 2011 anti-trafficking act, including failing to develop formal referral procedures, establish victim care centers, and complete a national action plan (2013)"
Introduction ::LesothoBackground:Basutoland was renamed the Kingdom of Lesotho upon independence from the UK in 1966. The Basuto National Party ruled the country during its first two decades. King MOSHOESHOE was exiled in 1990, but returned to Lesotho in 1992 and was reinstated in 1995 and subsequently succeeded by his son, King LETSIE III, in 1996. Constitutional government was restored in 1993 after seven years of military rule. In 1998, violent protests and a military mutiny following a contentious election prompted a brief but bloody intervention by South African and Batswana military forces under the aegis of the Southern African Development Community. Subsequent constitutional reforms restored relative political stability. Peaceful parliamentary elections were held in 2002, but the National Assembly elections of February 2007 were hotly contested and aggrieved parties disputed how the electoral law was applied to award proportional seats in the Assembly. In May 2012, competitive elections involving 18 parties saw Prime Minister Motsoahae Thomas THABANE form a coalition government - the first in the country's history - that ousted the 14-year incumbent, Pakalitha MOSISILI, who peacefully transferred power the following month.Geography ::LesothoLocation:Southern Africa, an enclave of South AfricaGeographic coordinates:29 30 S, 28 30 EArea:total: 30,355 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 142land: 30,355 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than MarylandLand boundaries:total: 909 kmborder countries: South Africa 909 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:temperate; cool to cold, dry winters; hot, wet summersTerrain:mostly highland with plateaus, hills, and mountainsElevation extremes:lowest point: junction of the Orange and Makhaleng Rivers 1,400 mhighest point: Thabana Ntlenyana 3,482 mNatural resources:water, agricultural and grazing land, diamonds, sand, clay, building stoneLand use:arable land: 10.14%permanent crops: 0.13%other: 89.72% (2011)Irrigated land:26.37 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:3.02 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 0.04 cu km/yr (46%/46%/9%)per capita: 21.79 cu m/yr (2000)Natural hazards:periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:population pressure forcing settlement in marginal areas results in overgrazing, severe soil erosion, and soil exhaustion; desertification; Highlands Water Project controls, stores, and redirects water to South AfricaEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:landlocked, completely surrounded by South Africa; mountainous, more than 80% of the country is 1,800 m above sea levelPeople and Society ::LesothoNationality:noun: Mosotho (singular), Basotho (plural)adjective: BasothoEthnic groups:Sotho 99.7%, Europeans, Asians, and other 0.3%,Languages:Sesotho (official) (southern Sotho), English (official), Zulu, XhosaReligions:Christian 80%, indigenous beliefs 20%Population:1,936,181 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 148note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 33.1% (male 322,189/female 319,618)15-24 years: 20.2% (male 185,931/female 205,643)25-54 years: 36.3% (male 344,120/female 359,370)55-64 years: 4.9% (male 50,781/female 44,399)65 years and over: 5.4% (male 52,241/female 51,889) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 68.3 %youth dependency ratio: 61.2 %elderly dependency ratio: 7.1 %potential support ratio: 14.1 (2013)Median age:total: 23.4 yearsmale: 23.3 yearsfemale: 23.4 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.34% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Birth rate:26.31 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Death rate:15.02 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Net migration rate:-7.89 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Urbanization:urban population: 27.6% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.57% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MASERU (capital) 220,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.9 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.14 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.99 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:21.2note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2009 est.)Maternal mortality rate:620 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 12Infant mortality rate:total: 51.93 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 38male: 55.96 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 47.78 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 52.3 yearscountry comparison to the world: 212male: 52.2 yearsfemale: 52.39 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.83 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Contraceptive prevalence rate:47% (2009/10)Health expenditures:11.1% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 18Physicians density:0.05 physicians/1,000 population (2003)Hospital bed density:1.33 beds/1,000 population (2006)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 91% of populationrural: 73% of populationtotal: 78% of populationunimproved:urban: 9% of populationrural: 27% of populationtotal: 22% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 32% of populationrural: 24% of populationtotal: 26% of populationunimproved:urban: 68% of populationrural: 76% of populationtotal: 74% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:23.6% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 3HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:290,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 20HIV/AIDS - deaths:14,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Obesity - adult prevalence rate:14.6% (2008)country comparison to the world: 120Children under the age of 5 years underweight:13.5% (2010)country comparison to the world: 56Education expenditures:13% of GDP (2008)country comparison to the world: 1Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 89.6%male: 83.3%female: 95.6% (2010 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 10 yearsmale: 10 yearsfemale: 10 years (2006)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 103,020percentage: 23 % (2000 est.)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 34.4%country comparison to the world: 17male: 29%female: 41.9% (2008)Government ::LesothoCountry name:conventional long form: Kingdom of Lesothoconventional short form: Lesotholocal long form: Kingdom of Lesotholocal short form: Lesothoformer: BasutolandGovernment type:parliamentary constitutional monarchyCapital:name: Maserugeographic coordinates: 29 19 S, 27 29 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:10 districts; Berea, Butha-Buthe, Leribe, Mafeteng, Maseru, Mohale's Hoek, Mokhotlong, Qacha's Nek, Quthing, Thaba-TsekaIndependence:4 October 1966 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 4 October (1966)Constitution:2 April 1993Legal system:mixed legal system of English common law and Roman-Dutch law; judicial review of legislative acts in High Court and Court of AppealInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: King LETSIE III (since 7 February 1996); note - King LETSIE III formerly occupied the throne from November 1990 to February 1995 while his father was in exilehead of government: Prime Minister Motsoahae Thomas THABANE (since 8 June 2012)cabinet: Cabinet(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: according to the constitution, the leader of the majority party, or coalition of parties, in the Assembly automatically becomes prime minister; the monarchy is hereditary, but, under the terms of the constitution that came into effect after the March 1993 election, the monarch is a ""living symbol of national unity"" with no executive or legislative powers; under traditional law the college of chiefs has the power to depose the monarch, determine who is next in the line of succession, or who shall serve as regent in the event that the successor is not of mature ageLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (33 members - 22 principal chiefs and 11 other members appointed by the ruling party) and the Assembly (120 seats, 80 by popular vote and 40 by proportional vote; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)elections: last held on 26 May 2012 (next to be held in 2017)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - DC 48, ABC 30, LCD 26, BNP 5, PFD 3, NIP 2, other 6Judicial branch:highest court(s): Court of Appeal (consists of the court president, such number of justices of appeal as set by Parliament, and the Chief Justice and the puisne judges of the High Court ex officio); High Court (consists of the chief justice and such number of puisne judges as set by Parliament); note - both the Court of Appeal and the High Court have jurisdiction in constitutional issuesjudge selection and term of office: Court of Appeal president and High Court chief justice appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister; puisne judges appointed by the monarch on advice of the Judicial Service Commission, an independent body of judicial officers and officials designated by the monarch; judges of both courts can serve until age 75subordinate courts: Magistrate Courts; customary or traditional courts; Courts MartialPolitical parties and leaders:All Basotho Convention or ABC [Motsoahae Thomas THABANE]Basotho Batho Democratic Party or BBDP [Geremane RAMATHEBANE]Basotho Congress Party or BCP [Thulo MAHLAKENG]Basotho Democratic National Party or BDNP [Thabang NYEOE]Basotho National Party or BNP [Thesele 'MASERIBANE]Democratic Congress or DC [Pakalitha MOSISILI]Lesotho Congress for Democracy or LCD [Mothetjoa METSING]Lesotho Peoples Congress or LPC [Kelebone MAOPE]Lesotho Workers Party or LWP [Macaefa BILLY]Marematlou Freedom Party or MFP [Vincent MALEBO]National Independent Party or NIP [Kimetso MATHABA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Media Institute of Southern Africa, Lesotho chapter [Tsebo MATŠASA] (pushes for media freedom)International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, SACU, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Eliachim Molapi SEBATANEchancery: 2511 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 797-5533FAX: [1] (202) 234-6815Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Carl B. FOXembassy: 254 Kingsway Road, Maseru West (Consular Section)mailing address: P. O. Box 333, Maseru 100, Lesothotelephone: [266] 22 312666FAX: [266] 22 310116Flag description:three horizontal stripes of blue (top), white, and green in the proportions of 3:4:3; the colors represent rain, peace, and prosperity respectively; centered in the white stripe is a black Basotho hat representing the indigenous people; the flag was unfurled in October 2006 to celebrate 40 years of independenceNational symbol(s):Basotho hatNational anthem:name: ""Lesotho fatse la bo ntat'a rona"" (Lesotho, Land of Our Fathers)lyrics/music: Francois COILLARD/Ferdinand-Samuel LAURnote: adopted 1967; the anthem's music derives from an 1823 Swiss songbookEconomy ::LesothoEconomy - overview:Small, mountainous, and completely landlocked by South Africa, Lesotho is a least developed country in which about three-fourths of the people live in rural areas and engage in subsistence agriculture. Lesotho produces less than 20% of the nation's demand for food. Rain-fed agriculture is vulnerable to weather and climate variability; an estimated 725,500 people will require food assistance in 2012/13. The distribution of income in Lesotho remains inequitable. Lesotho relies on South Africa for much of its economic activity. Lesotho imports 90% of the goods it consumes from South Africa, including most agricultural inputs. Households depend heavily on remittances from family members working in South Africa, in mines, on farms and as domestic workers, though mining employment has declined substantially since the 1990s. Government revenue depends heavily on transfers from South Africa. Customs duties from the Southern Africa Customs Union accounted for 44% of government revenue in 2012. The South African Government also pays royalties for water transferred to South Africa from a dam and reservoir system in Lesotho. However, the government continues to strengthen its tax system to reduce dependency on customs duties and other transfers. Access to credit remains a problem for the private sector. The government maintains a large presence in the economy - public expenditures accounted for 55% of GDP in 2010 and the government remains Lesotho's largest employer. Lesotho's largest private employer is the textile and garment industry - approximately 36,000 Basotho, mainly women, work in factories producing garments for export to South Africa and the US. Diamond mining in Lesotho has grown in recent years and may contribute 8.5% to GDP by 2015, according to current forecasts. Lesotho's $362.5 million Millennium Challenge Account Compact, which focused on strengthening the healthcare system, developing the private sector, and providing access to improved water supplies and sanitation facilities, will end in September 2013. Despite the 2008/09 global economic crisis, the economy has recovered strongly with growth averaging nearly 5% per year since 2010.GDP (purchasing power parity):$4.131 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 175$3.972 billion (2011 est.)$3.758 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$2.439 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 775.7% (2011 est.)6.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$2,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 191$2,100 (2011 est.)$2,000 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:21.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 679.4% of GDP (2011 est.)8.7% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 97.2%government consumption: 33.9%investment in fixed capital: 37.3%investment in inventories: -0.1%exports of goods and services: 50.9%imports of goods and services: -118.3%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 6.4%industry: 34.6%services: 59% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:corn, wheat, pulses, sorghum, barley; livestockIndustries:food, beverages, textiles, apparel assembly, handicrafts, construction, tourismIndustrial production growth rate:6.6% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Labor force:894,500 (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 86%industry and services: 14%note: most of resident population engaged in subsistence agriculture; roughly 35% of the active male wage earners work in South Africa (2002 est.)Unemployment rate:25% (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 17445% (2002 est.)Population below poverty line:49% (1999)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1%highest 10%: 39.4% (2003)Distribution of family income - Gini index:63.2 (1995)country comparison to the world: 156 (1986-87)Budget:revenues: $1.658 billionexpenditures: $1.536 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:68% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13Public debt:NAFiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchInflation rate (consumer prices):6.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1635% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:9.36% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2410% (31 December 2010 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:10.08% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8510.4% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$408.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 161$346.5 million (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$897 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 171$820.4 million (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$82.19 million (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 187$60.61 million (31 December 2010 est.)Current account balance:-$352.6 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 88-$521.5 million (2011 est.)Exports:$1.03 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 156$1.003 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:manufactures (clothing, footwear), wool and mohair, food and live animals, electricity, water, diamondsImports:$2.404 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 157$2.296 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:food; building materials, vehicles, machinery, medicines, petroleum productsReserves of foreign exchange and gold:$1.023 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 134$954.5 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$778.6 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 166$791.9 million (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$242 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 100$120 million (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:maloti (LSL) per US dollar -8.2031 (2012 est.)7.26 (2011 est.)7.32 (2010 est.)8.47 (2009)7.75 (2008)Energy ::LesothoElectricity - production:200 million kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 181Electricity - consumption:293 million kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Electricity - imports:121 million kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Electricity - installed generating capacity:76,000 kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Electricity - from fossil fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 149Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 156Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 155Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 197Refined petroleum products - consumption:1,777 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Refined petroleum products - imports:1,813 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 155Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 134Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 159Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:282,100 Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 190Communications ::LesothoTelephones - main lines in use:38,600 (2011)country comparison to the world: 168Telephones - mobile cellular:1.232 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 152Telephone system:general assessment: rudimentary system consisting of a modest number of landlines, a small microwave radio relay system, and a small radiotelephone communication system; mobile-cellular telephone system is expandingdomestic: privatized in 2001, Telecom Lesotho was tasked with providing an additional 50,000 fixed-line connections within five years, a target not met; mobile-cellular service dominates the market and is expanding with a subscribership roughly 65 per 100 persons in 2011; rural services are scantinternational: country code - 266; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:1 state-owned TV station and 2 state-owned radio stations; government controls most private broadcast media; satellite TV subscription service available; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters obtainable (2008)Internet country code:.lsInternet hosts:11,030 (2012)country comparison to the world: 131Internet users:76,800 (2009)country comparison to the world: 168Transportation ::LesothoAirports:24 (2013)country comparison to the world: 132Airports - with paved runways:total: 3over 3,047 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 21914 to 1,523 m: 5under 914 m:16 (2013)Roadways:total: 7,091 kmcountry comparison to the world: 146paved: 1,404 kmunpaved: 5,687 km (2003)Military ::LesothoMilitary branches:Lesotho Defense Force (LDF): Army (includes Air Wing) (2012)Military service age and obligation:18-24 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; women serve as commissioned officers (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 472,456females age 16-49: 508,953 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 270,184females age 16-49: 275,734 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 19,110female: 20,037 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.9% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 70Military - note:Lesotho's declared policy is maintenance of its independent sovereignty and preservation of internal security; in practice, external security is guaranteed by South Africa; restructuring of the Lesotho Defense Force (LDF) and Ministry of Defense and Public Service over the past five years has focused on subordinating the defense apparatus to civilian control and restoring the LDF's cohesion; the restructuring has considerably improved capabilities and professionalism, but the LDF is disproportionately large for a small, poor country; the government has outlined a reduction to a planned 1,500-man strength, but these plans have met with vociferous resistance from the political opposition and from inside the LDF (2008)Transnational Issues ::LesothoDisputes - international:South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migrationTrafficking in persons:current situation: Lesotho is a source, transit, and destination country for women and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking and for men subjected to forced labor; Basotho women and children are subjected to domestic servitude and children, to a lesser extent, commercial sexual exploitation within Lesotho and South Africa; some Basotho women willingly migrate to South Africa seeking work in domestic service only to be forced into prostitution; some Basotho men who voluntarily migrate to South Africa for work become victims of forced labor in agriculture and mining or are coerced into committing crimestier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Lesotho does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government has decreased its anti-trafficking law enforcement and victim protection efforts during 2012; authorities have initiated fewer prosecutions, ceased arresting suspected trafficking offenders due to a backlog of prosecutions, and stopped referring victims to NGO centers for care; the government has not implemented key portions of the 2011 anti-trafficking act, including failing to develop formal referral procedures, establish victim care centers, and complete a national action plan (2013)"
The World Factbook. 2014.
